The ever-evolving landscape of Mac malware continues to raise concerns among users, with cybercriminals relentlessly exploring new avenues to compromise the security of these systems. One recent and concerning example is Search Alpha, a malicious strain that hijacks web browsers on Mac devices, redirecting users to unexpected search engines and websites. This article aims to shed light on the deceptive tactics employed by Search Alpha authors, the link to its notorious predecessor Search Marquis Mac virus, and the mechanisms that make it a persistent and tenacious threat on macOS.
The Search Alpha phenomenon
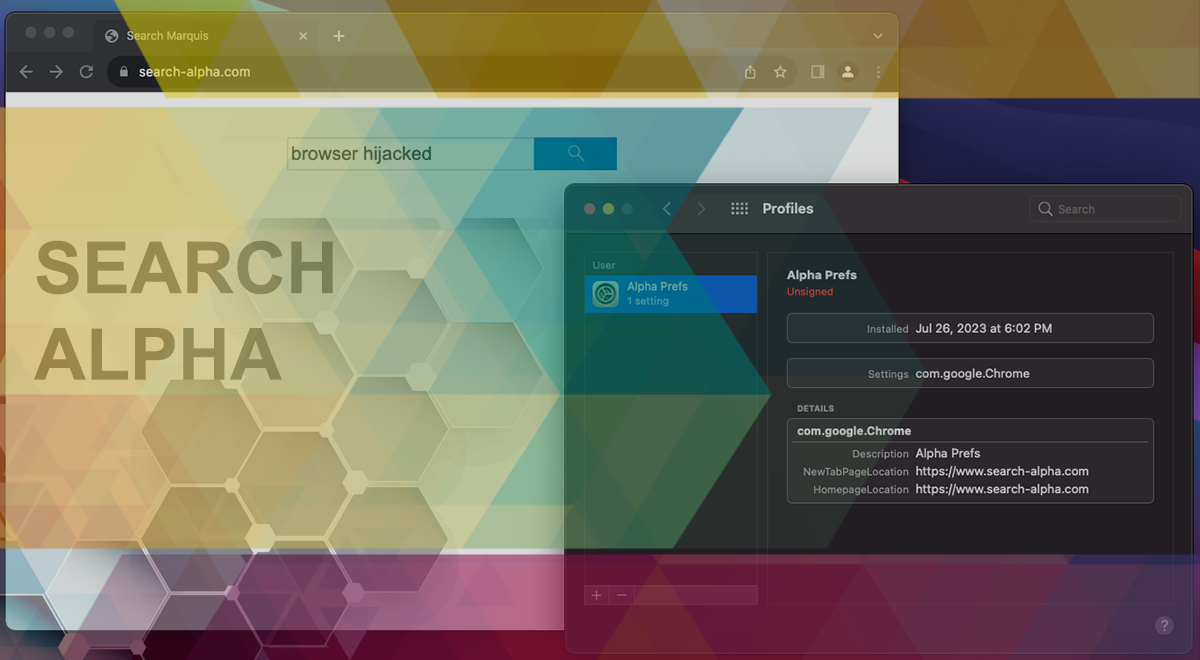
Search Alpha represents a growing menace in the realm of Mac malware, leaving users vulnerable to browser hijacking and unwarranted redirection. Upon infection, this insidious strain manipulates web browsers, forcing unsuspecting users to visit Bing or nearbyme.io websites through intermediary URLs associated with advertising networks’ APIs. The latter aspect allows the cybercriminals behind Search Alpha to diversify their attack monetization, making it an even more lucrative endeavor.
The legacy of Search Marquis Mac virus
Search Alpha is not a standalone phenomenon; it stands as a successor to the infamous Search Marquis Mac virus. The long-standing Search Marquis culprit wreaked havoc on the Mac community by redirecting victims’ browsers to searchmarquis.com, compromising their browsing experience and exposing them to potential risks.
With the emergence of Search Alpha, it becomes evident that cybercriminals have evolved their malicious techniques, demonstrating their determination to exploit Mac users and evade detection.
Distribution techniques of Search Alpha redirect virus
To reach its potential victims, the authors of Search Alpha employ a range of distribution techniques, capitalizing on the unsuspecting nature of users. Some common methods include:
- Malicious websites and ads: Search Alpha may be distributed through malicious websites or deceptive online ads, leading users to download seemingly legitimate software or updates that, in reality, harbor the malware.
- Software bundling: The malware creators may bundle Search Alpha with seemingly harmless software or applications, tricking users into unwittingly installing the malicious program.
- Fake updates: Cybercriminals may resort to fake software update alerts, urging users to download critical updates that, unbeknownst to them, contain the Search Alpha malware.
- Phishing emails: Phishing emails with malicious attachments or links might also be utilized as a means to deliver Search Alpha to potential targets.
Persistence mechanisms in the repertoire of Search Alpha
To ensure its tenacity on infected Mac systems, Search Alpha establishes persistence through two primary mechanisms:
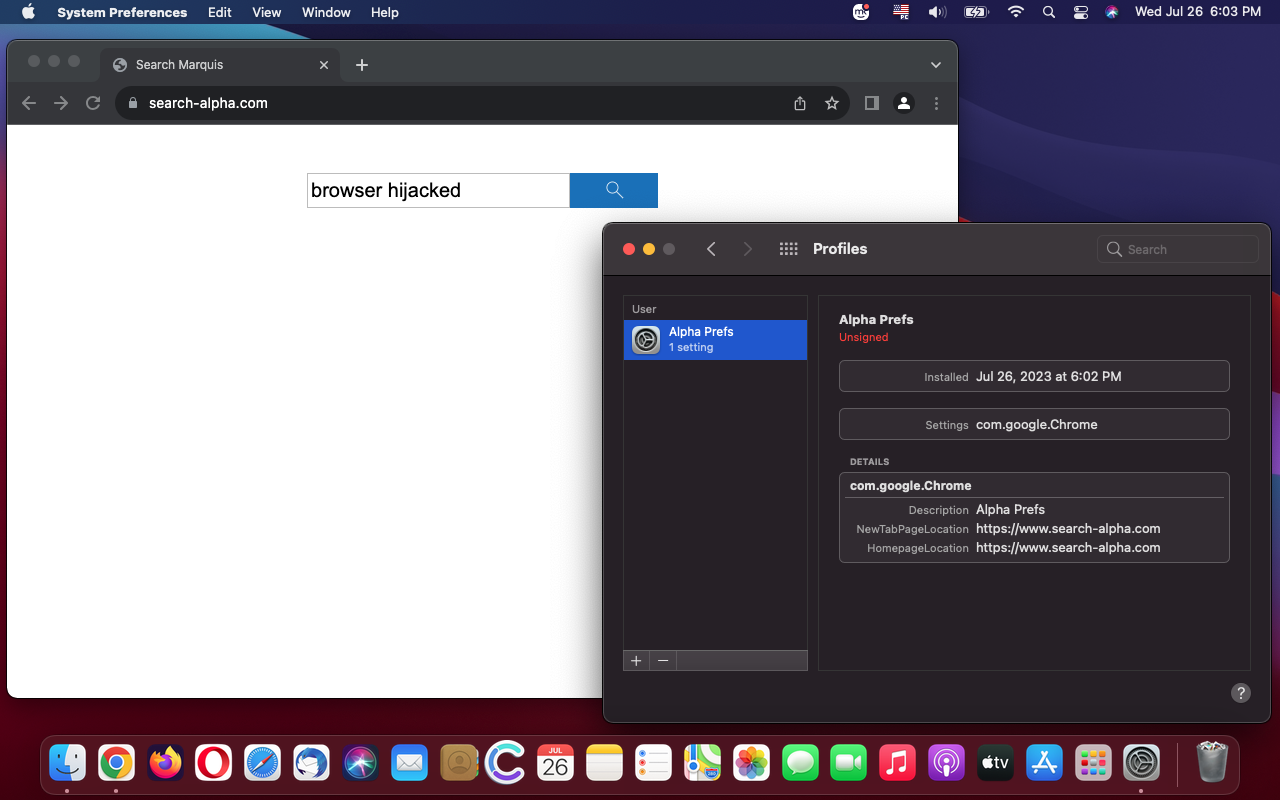
- Rogue configuration profiles: The malware creates a rogue configuration profile, granting it privileges and control over the device’s settings. This manipulation allows Search Alpha to maintain a foothold on the system, making it challenging for users to remove the malware entirely.
- Dubious Launch Agents and Launch Daemons: Search Alpha spawns dubious launch agents and launch daemons, ensuring that the malware activates upon system boot. By infiltrating these legitimate system components, the malware evades detection, sustaining its malicious activities across multiple system restarts.
It’s better to be protected than not
The emergence of Search Alpha serves as a stark reminder of the relentless pursuit of cybercriminals to exploit Mac vulnerabilities. With its deceptive browser hijacking and redirection tactics, this malware poses significant risks to the security and privacy of Mac users.
Rooted in the legacy of the notorious Search Marquis Mac virus, Search Alpha represents a new chapter in the evolving saga of Mac malware. Its distribution techniques, persistence mechanisms, and intermediary URLs associated with advertising networks’ APIs showcase the malicious ingenuity of its creators.
To safeguard against such threats, Mac users must remain vigilant, practice secure online habits, and refrain from downloading software from unverified sources. Utilizing reputable security software, promptly updating software and system, and exercising caution while handling email attachments or suspicious links are vital steps in maintaining a resilient defense against malicious strains like Search Alpha.
As the battle between cybersecurity defenders and cybercriminals continues, user awareness and proactive cybersecurity measures will remain critical in mitigating the risks posed by emerging Mac malware threats like the one under scrutiny By staying informed, adopting best security practices, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity, Mac users can fortify their defenses and protect their digital lives from the clutches of these cunning adversaries.